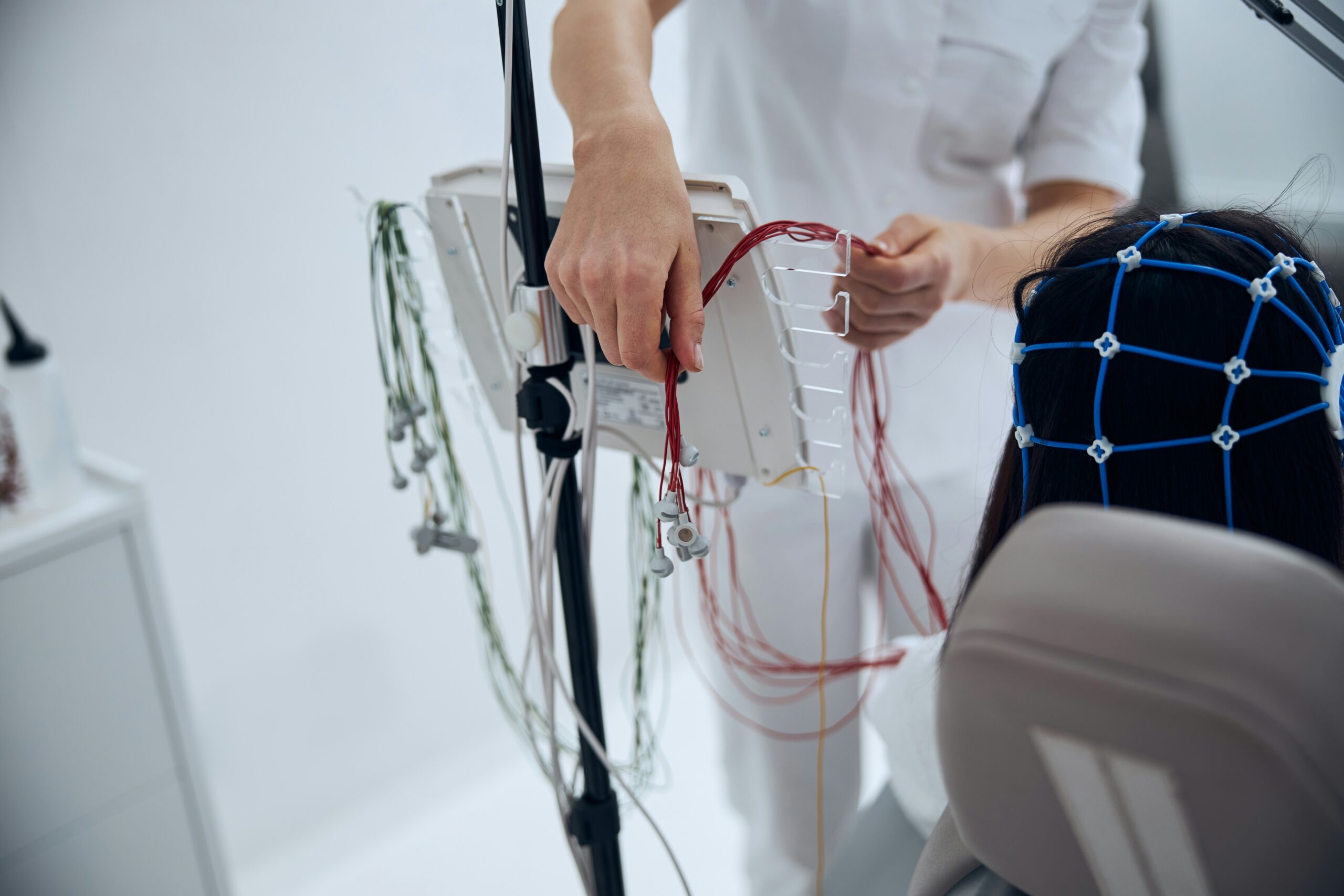
Neurological disorders have long been some of the most challenging conditions to treat. Millions of people worldwide suffer from diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis, with treatment options historically limited to symptom management. However, thanks to recent advancements in research, technology, and innovative therapies, the future of neurological treatment is brighter than ever before. Breakthroughs in gene therapy, stem cell research, and neurostimulation offer new hope to patients, and the field of neurology is breaking new ground in ways that could change lives forever.
New Technologies Leading the Way
Technological advancements drive the rapidly evolving landscape of neurological treatment. These innovations have enabled targeted treatments to address the root causes of many neurological conditions rather than just alleviating symptoms. As these technologies continue to improve, we see therapies that offer real, tangible patient benefits.
Neurostimulation is one of the most promising technologies currently transforming the treatment of neurological disorders. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a prime example of this innovation. Electrical impulses can regulate abnormal brain activity by implanting a small device into the brain. DBS is particularly effective for patients with Parkinson’s disease, reducing symptoms such as tremors and rigidity. This technology offers a more dynamic solution to managing these conditions than traditional medications, which often lose effectiveness over time.
Additionally, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is gaining traction as a non-invasive method for treating depression, migraines, and other neurological conditions. Using magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain areas, TMS can help patients who have not responded well to medication.
The Promise of Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is one of the most revolutionary approaches in modern medicine, and it holds enormous potential in treating neurological diseases. Gene therapy involves introducing, removing, or altering genetic material within a patient’s cells to treat or prevent disease. For neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease or Huntington’s disease, gene therapy can potentially correct the faulty genes responsible for disease progression.
Recent studies have shown promising results in treating Parkinson’s disease with gene therapy. Researchers are investigating how to use viral vectors to deliver healthy copies of the genes that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter crucial for motor function. The goal is to restore the dopamine-producing cells in the brain, offering a long-term solution to the motor issues that define Parkinson’s disease. Although gene therapy is still experimental, early trials have demonstrated the potential to slow disease progression and improve patient outcomes.
Another area where gene therapy shows potential is in treating epilepsy. Researchers are working to develop gene therapies that can alter the genetic mutations causing seizures in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. If successful, this approach could eliminate the need for lifelong medication and cure many patients.
Stem Cell Research: Revolutionizing Neurological Treatment
Stem cell therapy is another groundbreaking area of research in neurology. These cells can uniquely differentiate into various types of cells, including neurons. As a result, they offer a powerful tool in regenerative medicine, particularly for patients with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or multiple sclerosis.
Replacing damaged neurons with healthy ones offers the possibility of reversing the damage caused by these devastating conditions. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, researchers are investigating the potential of stem cells to regenerate dopamine-producing neurons, the loss of which leads to motor dysfunction. Initial studies have shown that stem cells can be successfully transplanted into the brain, where they can begin to produce dopamine, alleviating some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Similarly, stem cells could be used to rebuild this protective layer for patients with multiple sclerosis, which involves the degradation of the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibers. This would help restore nerve function and slow the progression of the disease.
While stem cell therapies are still in the experimental phase, their potential to transform the treatment of neurological disorders cannot be overstated. As research continues and clinical trials expand, stem cell therapies are expected to become a more widely accessible treatment option.
Advances in Epilepsy Treatment: New Hope for Patients
Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder that affects millions worldwide. Although anti-seizure medications are the first line of treatment, they do not work for everyone. For patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, new treatment options are crucial.
Responsive neurostimulation (RNS) is one of the most promising advancements in epilepsy treatment. RNS involves the implantation of a small device in the brain that detects abnormal electrical activity and delivers electrical pulses to prevent seizures from occurring. Early studies have shown that RNS can significantly reduce the frequency of seizures in patients with difficult-to-control epilepsy. This approach offers hope to individuals who have been living with uncontrolled seizures for years.
In addition to RNS, laser ablation therapy is a minimally invasive procedure being used to treat epilepsy. Laser ablation involves using a laser to destroy the small area of brain tissue that causes seizures. This technique is particularly effective for patients with focal epilepsy, where seizures originate in one specific part of the brain. It provides an option for patients not candidates for traditional surgery, offering a safer and less invasive alternative.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatment to the Individual
One of the most exciting trends in neurological treatment is the rise of personalized medicine. This approach involves tailoring treatments to the individual patient based on their unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. By analyzing a patient’s genetic information, doctors can develop more targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective and have fewer side effects.
In neurology, personalized medicine has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. For example, researchers investigate how genetic testing can identify patients more likely to respond to specific treatments, allowing doctors to prescribe the most effective medications or therapies right from the start.
Moreover, personalized medicine can help avoid the trial-and-error approach often accompanying neurological treatment. By predicting which therapies will work best for a patient, doctors can reduce the time it takes to find the right treatment, improving outcomes and minimizing unnecessary side effects.
Future of Neurological Treatment: A New Era of Hope
The future of neurological treatment is incredibly promising, with advancements in gene therapy, stem cell research, neurostimulation, and personalized medicine opening up new possibilities for patients. As research in these fields progresses, more effective and targeted therapies are likely to become available, offering hope to individuals with neurological disorders.
Although many challenges exist, including the need for further clinical trials and the refinement of treatment methods, the progress has been remarkable. With continued investment in research and innovation, the potential to dramatically improve the lives of millions of people living with neurological conditions is within reach.
As we break new ground in neurological treatment, we improve patients’ lives today and pave the way for future generations to live healthier, longer lives free from the debilitating effects of neurological diseases.